[paper-review] Promptable Behaviors: Personalizing Multi-Objective Rewards from Human Preferences
Arxiv. [Paper] [Project Page]
Minyoung Hwang1, Luca Weihs1, Chanwoo Park2, Kimin Lee3, Aniruddha Kembhavi1, Kiana Ehsani1 > 1PRIOR @ Allen Institute for AI, 2Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 3Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
Dec. 14
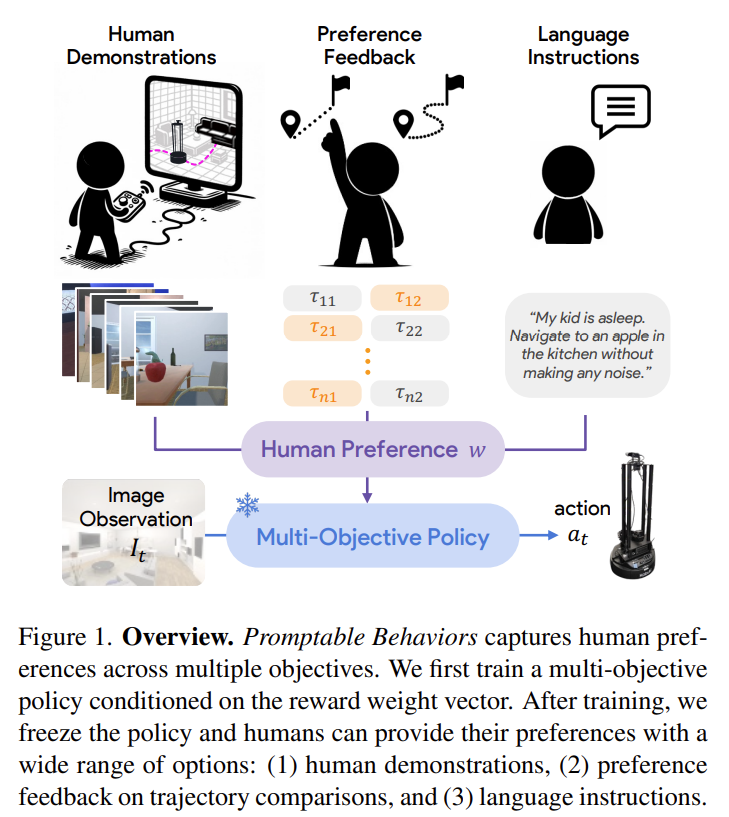
Fig. 1: Overview of PromptableBehavior.
한 문장 요약
- promptable navigation behavior 연구를 선보였다.
Contribution
- 기존의 Embodied AI에서 hand-crafted reward design이 어려웠음.
- Novel framework를 제시함: simplify the reward design process
- 3개의 interaction type을 통해 human preference를 추론했다.
- (1) human demonstration, (2) preference feedback on trajectory comparison, (3) language instructions
- ProcTHOR, RoboTHOR에서 실험을 수행함.
Problem Formulation
- 가정하고 있는 점은 아래와 같음.
- Human preference remains constant over time
- Each human preference is captured through a linear combination of multiple objectives in the environment
- 매 timestep t 마다 agent는 RGB observation \(o_t\)에 기반한 action \(a_t\)를 뱉어낸다.
- action은
[MoveAhead, RotateRight, RotateLeft, Done, LookUp, LookDown]이 있음.
- action은
- 저자는 여기서
agent’s (navigation) behavior에 집중해, preference로 표현해주려고 함.
Methodology: Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning (MORL)
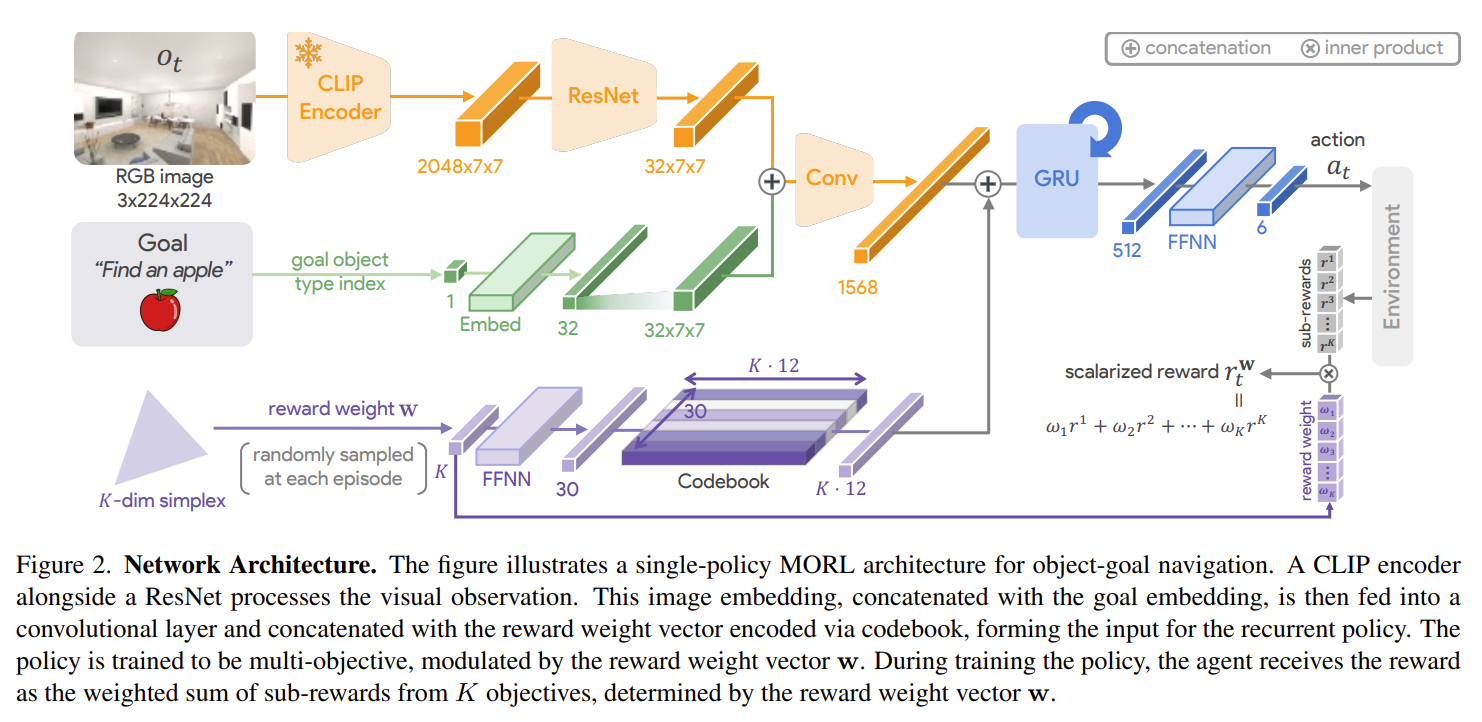
Fig. 2: Architecture of PromptableBehavior.
Build Scene Representation
- multiple objective를 갖는 policy를 학습함. (conditioned on a reward weight vector)
- (이는 Ask4Help 논문에서 영감을 얻었다고 함)
- reward weight vector를 human preference에 일치하게 infer하도록 함. 이러한 reward weight에 대해서 추가적인 fine-tuning 없이 preference 조작이 가능함.
- 저자가 제시하는 Promptable Behaviors는 2가지 단계로 이루어짐.
- (1) Training a promptable multi-objective policy
- (2) Capturing the agent’s desired behavior through interactions.
- Image encoding에는 CLIP 모델을 사용함.
- Reward weight encoder로는 feed-forward neural network(FFNN)을 활용해, \(K \cdot 12\)-dim latent codebook으로 표현함.
- \(r^{\mathbf{w}}=\mathbf{w^{\intercal}r}\),
-
\(\mathbf{w}\): randomly sampled from \(K\)-dim simplex $$\Delta_K={\mathbf{w} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}_{+} ~ \mathbf{w} _{1}=1}$$ - 기존의 연구들은 \(\mathbf{w}\)가 pre-defined 되어 있었지만, 저자는 이를 randomly exploration하겠다는 목적임. (그리고 이 reward weight vector \(\mathbf{w}\in\Delta_K\)인 user’s true preference로 표현된다고 가정한다.)
-
- \(r^{\mathbf{w}}=\mathbf{w^{\intercal}r}\),
- Navigation policy: DD-PPO 모델로 수행함.
Types of Interaction: reasoning through interactions
(1) Human Demonstration
- demonstrated action과 action distribution from policy \(\pi\) 간의 log-likelihood loss로 계산함.
(2) Trajectory Comparison
- 일반적인 Bradley-Terry 구조로 수행함.
(3) Language Instruction
- 사용자가 제시하는 task description과 definition of objective를 토대로 ChatGPT가 optimal reward weight vector 값을 뱉어주도록 하였음. (In-Context Learning, Chain-of-Thought로 수행함.)
- Objective sets:
time efficiency, path efficiency, house exploration, safety
Experiments
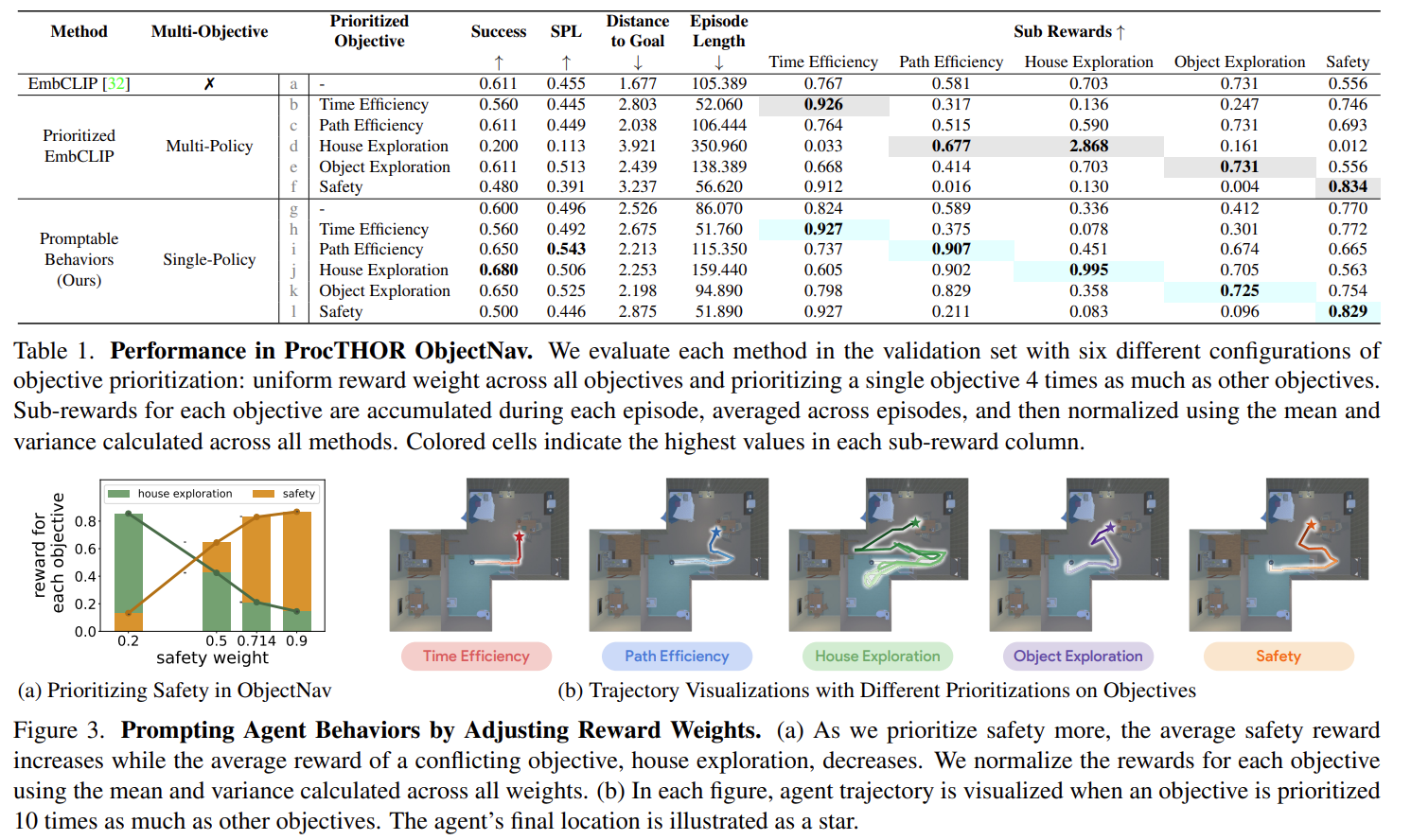
Fig. 3: Results of PromptableBehavior.
Thoughts:
- 제가 생각하는 preference의 정의는 해당 논문에서 표현하듯, agent behavior에 기반한 것과 더 근접하다고 생각합니다.
- 현재 저도 진행 중인 연구에 대해서 GPT-4V 모델이 human preference를 추론해주는 것만으로 contribution을 내세우기에는 어려움이 있을 것 같다고 여겨집니다.
- 저도 계속 구상해오던 점은, 해당 논문에서 수행한 것처럼 (1) 어떠한 reward policy를 학습하거나, (2) GPT가 preference weight를 뱉어주도록 하는 방향으로 수행하면 어떨까 라는 생각이 들었습니다. manipulator scene에 대해서도 충분히 arm motion에 대한 objective set을 정의해, 그에 따른 trajectory 결과도 보여줄 수 있을 것이라 생각합니다.
- 기존의 다른 preference-based RL 논문과 비교해 이 논문이 새로웠던 점은, K-dim reward weight에 대해 학습해주는 과정이라고 생각합니다.
- 이를 통해 기존에는 pre-defined and fixed w에 대해 수행된 것과 다르게, reward weight에 대해 exploration을 수행할 수 있었다고 생각합니다. (+ codebook representation)
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: