[paper-review] 6-DOF GraspNet: Variational Grasp Generation for Object Manipulation
Arsalan Mousavian, Clemens Eppner, Dieter Fox NVIDIA
17 Aug 2019
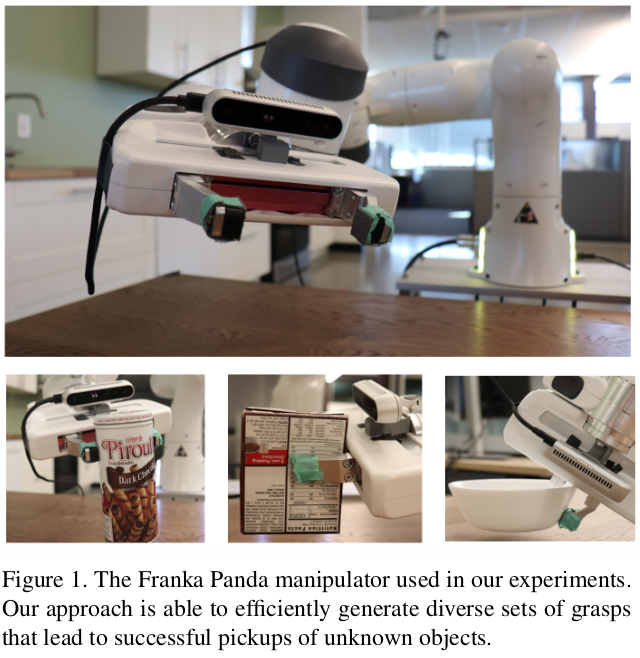
Fig. 1: Introduction figure about 6-dof graspnet paper.
Summary
The paper addresses the challenge of robotic object manipulation, specifically the generation of grasp poses. The author formulates the problem as sampling a set of grasps using a variational autoencoder (VAE) and refining these grasps with a grasp evaluator model. The key contribution of the approach is to generate diverse and stable grasps of unknown objects using 3D point clouds from a depth camera.
Methodology:
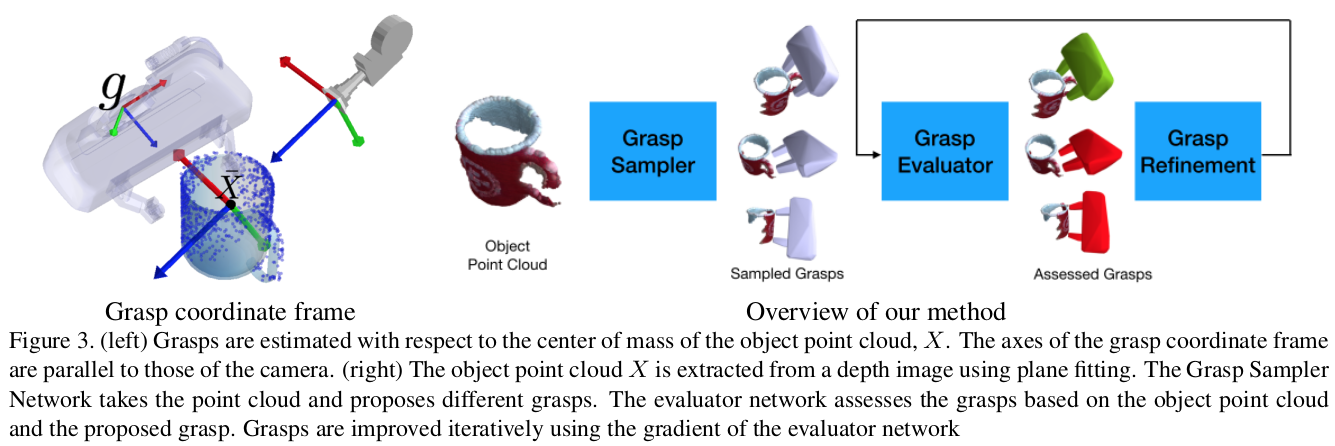
Fig. 2: Overall framework about 6-dof graspnet.
The author introduces a two-fold architecture: (1) a VAE for sampling diverse grasps and (2) a grasp evaluator network for refining these grasps. The VAE is trained to map partial point clouds of objects to a diverse set of grasps. The evaluator assesses and refines these grasps based on grasp quality.
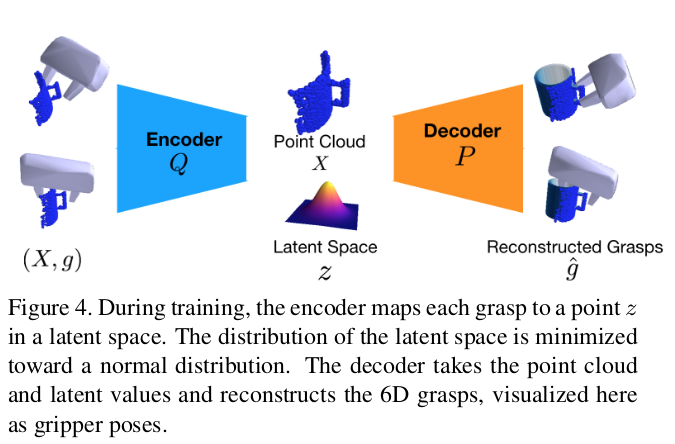
Fig. 3: VAE network about 6-dof graspnet.
Network Architecture: Training is conducted using simulated data for grasp generation. The network is based on the PointNet++ architecture, which effectively handles 3D point cloud data. After initial grasp generation, the grasps are iteratively refined using the evaluator network, enhancing both the success rate and the diversity of the grasps.
Experiments & Evaluation:

Fig. 4: Environmental setting about 6-dof graspnet.
Simulation-Based Training: The model is trained using data generated from physics simulations, FleX, ensuring a wide range of object shapes and grasp types. Real-World Robot Experiments: The author tests the model in real-world scenarios with a Franka Panda manipulator. The experiments involve picking up various objects, demonstrating the model’s ability to generate successful grasps in a physical environment. Evaluation Metrics: The success rate and coverage rate of grasps are used as metrics, with the model showing high performance in both aspects.
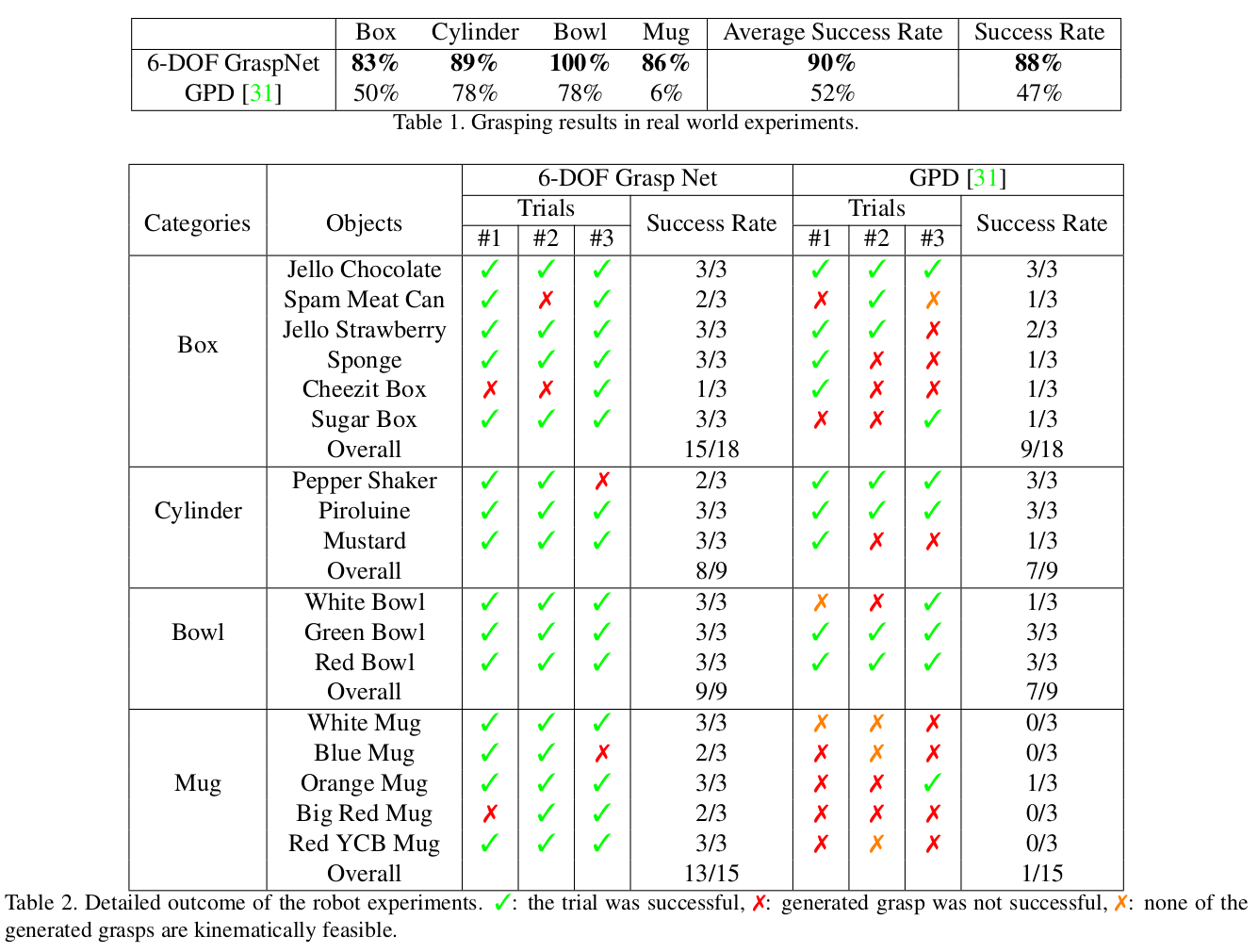
Fig. 5: Result Table.
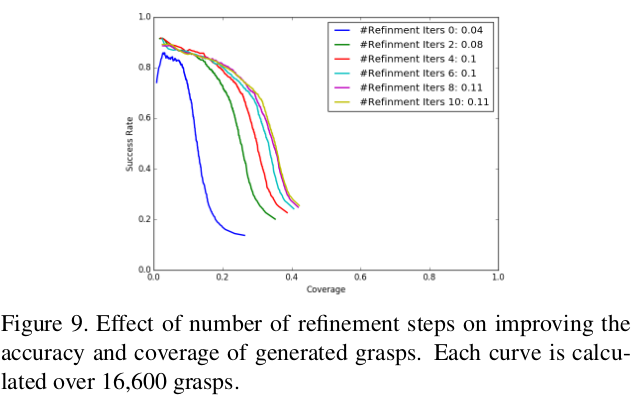
Fig. 6: Result of Refinement Network.
Conclusion:
This paper makes a significant step in robotic grasp generation by combining deep learning with physics simulator to obtain efficient, diverse, and successful grasps for object manipulation. The model’s success in both simulated and real-world tests underlines its potential for broad applications in robotics.
Thoughts:
The author presents an innovative approach to robotic grasp generation using a variational autoencoder and a grasp evaluator to handle a wide range of objects. The paper is the first to introduce both a learning-based method for generating grasp poses (i.e., learned grasp sampler) and a gradient-based optimization technique for improving these grasp poses (i.e., gradient-based refinement process). Trained with simulated data and validated with real-world experiments, the model effectively generates and refines grasp poses using 3D point clouds. Despite its reliance on simulated data, the paper shows a significant advancement in robotic manipulation, demonstrates practical applications.
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: