[paper-review] CoPa: General Robotic Manipulation through Spatial Constraints of Parts with Foundational Model
ArXiv, 2024. [Paper] [Project]
Haoxu Huang2,3,4*, Fanqi Lin1,2,4*, Yingdong Hu1,2,4, Shengjie Wang1,2,4, Yang Gao1,2,4 > 1Institute of Interdisciplinary Information Sciences, Tsinghua University. 2Shanghai Qi Zhi Institute. 3Shanghai Jiao Tong University. 4Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. * The first two authors contributed equally.
Mar. 13.
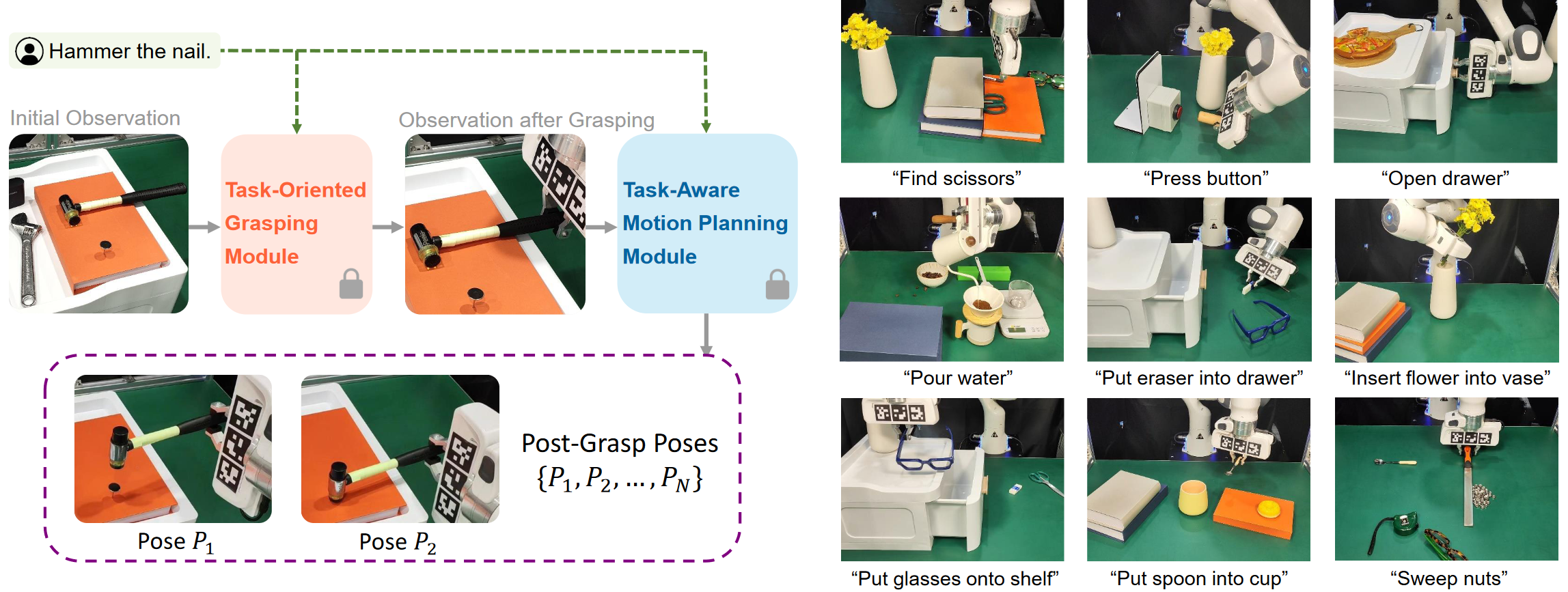
Fig. 1: Overview of CoPa.
Title
CoPa: General Robotic Manipulation through Spatial Constraints of Parts with Foundational Model (2024, ArXiv)
Summary:
- They introduce a framework CoPa, which generates a sequence of 6-DoF end-effector poses for open-world robotic manipulation.They introduce a framework CoPa, which generates a sequence of 6-DoF end-effector poses for open-world robotic manipulation.
Contributions.
- Task-Oriented Grasping Module
- Firstly, they annotate the grasping object leveraging SoM method. (Coarse-Grained Object Grounding)
- Sequentially crop the image into the region of interest (ROI) of the grasped object. Annotate the grasp contact point in the pixel coordinates of the image. Take a sample grasp pose from GraspNet and match it to the annotated contact point. (Fine-grained part grounding)
- Task-Aware Motion Planning Module
- This module is used to obtain a series of post-grasp poses. Given the instruction and the current observation, they first employ a grounding module to identify task-relevant parts within the scene.
- Subsequently, these parts are modeled in 3D, and are then projected and annotated onto the scene image. Following this, VLMs are utilized to generate spatial constraints for these parts. Finally, a solver is applied to calculate the post-grasp poses based on these constraints.
Thoughts.
- They presented their methodology in a very clear way: Combine (I) high-level task planning, which determines what to do next, and (ii) low-level robotic control, focusing on the precise actuation of joints.
- Now the GPT-X model can be used in robotic tasks to think like a human.
- They demonstrate the seamless integration with ViLa to accomplish long-horizon tasks.
- The high-level planner generates a sequence of sub-goals, which are then executed by CoPa.
- The results show that CoPa can be easily integrated with existing high-level planning algorithms to accomplish complex, long-horizon tasks.
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: